Fossil analysis reveals how Denisovans thrived on the ‘roof of the world’

[ad_1]
Editor’s note: A version of this story appeared in CNN’s Wonder Theory science newsletter. To get it in your inbox, sign up for free here.
CNN
—
The grasslands, glaciers and snow-tipped peaks of the Tibetan Plateau are breathtaking, but the vast expanse in Central Asia is also one of Earth’s harshest environments.
When I traveled to the plateau three decades ago, my head pounded, and I got sluggish from altitude sickness.
Archaeologists long believed the Tibetan Plateau — more than 13,000 feet (about 4,000 meters) above sea level — was one of the last places on the planet to be settled.
But new research suggests a mysterious species of ancient human was able to thrive on the so-called roof of the world well before Homo sapiens, our own species, arrived on the scene.

Researchers first identified Denisovans in 2010 using DNA sequences extracted from a rare tiny fragment of finger bone found in Siberia.
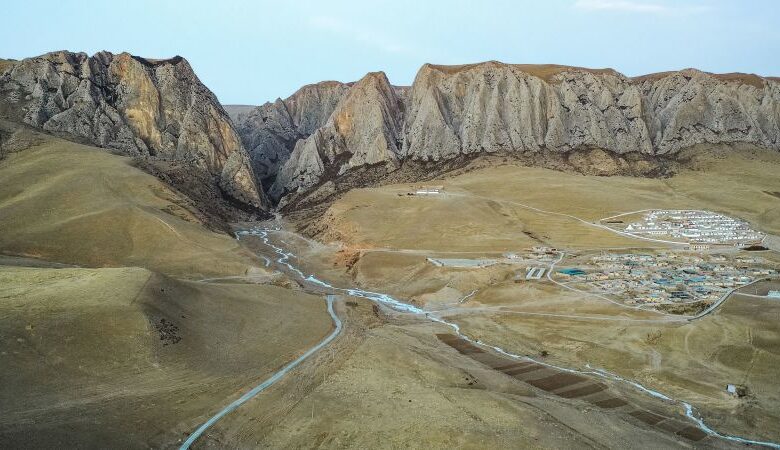
Now, Baishiya Karst Cave, on the northeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau, is helping answer many questions about who the Denisovans were.
Archaeologists have examined a jaw and rib bone found at the cave site, along with thousands of animal bone fragments retrieved during excavations in 2018 and 2019.
The analysis is shedding light on how the extinct humans thrived in the ice age environment for more than 100,000 years.
With the June 25 return of the Chang’e-6 lunar mission, the government of China possesses something no other humans have encountered — rocks and soil from the far side of the moon.
The China National Space Administration has said it will again share its lunar samples with scientists around the world — following the precedent NASA set after the Apollo missions.
But a US law known as the Wolf Amendment, which prohibits the use of government funds by NASA for bilateral cooperation with China or its agencies without authorization from Congress or the FBI, may stymie US access to the samples.
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson told CNN this week that the federal agency was working to make sure that accessing the lunar soil samples would not violate the law. Results from the analysis of the samples could help scientists peer back into the early days of the moon, Earth and the solar system.

Take a moment to marvel at what researchers say is the world’s oldest known story. Painted on a cave wall in what’s now Indonesia, it depicts three humans interacting with a pig.
The research team used a new technique to date the calcium carbonate crust that formed over the art to more than 50,000 years old.
The discovery is the latest rock art to be found in the region’s intriguing limestone caves and is at least 33,000 years older than Europe’s famed Paleolithic sites such as Lascaux.
Some experts think the paintings could have been a visual complement to oral stories lost to time.
Rivers often change course as they flow. But a research team studying the Ganges, which snakes its way from the Himalayas through India and Bangladesh, found evidence of something much more dramatic in its ancient past.
From clues hidden in mud and grains of sand, scientists gleaned that a powerful earthquake rerouted the river 2,500 years ago — the first time this natural phenomenon has been detected.
The team found sand volcanoes — a hallmark of a riverbed affected by a quake — and a large river channel that filled with mud at roughly the same time.
If a similar earthquake happened in the Ganges Delta today, more than 140 million people in the area could be affected.

Entomologist Dr. Gerard Talavera came across 10 painted lady butterflies on a beach about a decade ago in French Guiana. With torn wings peppered with holes, the insects appeared worn out.
While a painted lady is a hardy long-distance traveler, with migration patterns that stretch for thousands of miles, it usually travels over land so it can stop and rest.
Talavera, a senior researcher at the Botanical Institute of Barcelona in Spain, suspected the butterflies had crossed the Atlantic Ocean without stopping. In a new study, he and an international team have pieced together what it took to make such an epic journey.
In other insect news, researchers have spotted ants amputating the infected limbs of wounded nestmates.
Dig into these thought-provoking reads.
— The rotation of Earth’s core has been slowing over the past few decades, a recent study confirmed. Here’s what that could mean.
— Paleontologists uncovered fossils of a giant swamp creature with a toilet seat-shaped skull that was likely a top predator 40 million years before dinosaurs appeared on Earth.
— The discovery of fossilized grape seeds has revealed why you have the dinosaurs’ demise to thank for your glass of red wine.
— A Massachusetts woman who had lost a limb following a 2018 accident is walking and moving like anyone else now that she has a bionic leg fully connected to her brain.
— A new NASA radar image shows a tiny moon around an asteroid as it made a close pass of Earth.
Like what you’ve read? Oh, but there’s more. Sign up here to receive in your inbox the next edition of Wonder Theory, brought to you by CNN Space and Science writers Ashley Strickland and Katie Hunt. They find wonder in planets beyond our solar system and discoveries from the ancient world.
[ad_2]
Source link